
Snowflake ha semplificato l'integrazione dei modelli di machine learning nelle data application grazie a comode funzionalità che consentono di distribuire i modelli ML come stored procedure, User Defined Function (UDF) e User Defined Table Function (UDTF). Inoltre offre la Snowflake SQL API, un'API RESTful che facilita l'interrogazione dei modelli ML distribuiti e consente un'integrazione trasparente tra l'applicazione e il modello ML.
In questo tutorial, stai creando un'applicazione che aiuta l'azienda fittizia di food truck Tasty Bytes e i suoi conducenti a visualizzare i suggerimenti sulle posizioni forniti dal modello ML direttamente nella data application. Questo modello ML per i suggerimenti sulle posizioni è stato creato all'interno di Snowflake utilizzando Snowpark, che consente agli utenti Python di sfruttare con facilità la piattaforma Snowflake. Il modello utilizza i dati storici sulle vendite e dati meteorologici offerti da SafeGraph tramite il Marketplace Snowflake per fornire più informazioni al modello. Questo tutorial ti guiderà nel processo di distribuzione e integrazione del modello ML nell'app per i conducenti dei food truck.
Prerequisiti
- I privilegi necessari per creare un utente, un database e un warehouse in Snowflake
- La possibilità di installare ed eseguire software sul tuo computer
- Esperienza di base nell'uso di git
- Conoscenza di SQL a livello intermedio
- Accesso per eseguire SQL in Snowflake
Cosa imparerai
- Come accedere ai dati di terze parti dal Marketplace Snowflake
- Come addestrare un modello in Snowflake con una stored procedure
- Come distribuire un modello in Snowflake sotto forma di User Defined Function per l'inferenza del modello
- Come integrare un modello ML nella data application
Cosa ti serve
Cosa realizzerai
- Una data application alimentata da un modello ML utilizzando Snowpark
Utilizzerai Snowsight, l'interfaccia web di Snowflake, per:
- Accedere ai dati sulle posizioni di SafeGraph dal Marketplace Snowflake
- Creare oggetti Snowflake (warehouse, database, schema)
- Caricare dati sulle vendite per turno da S3
- Unire le vendite per turno con i dati sulle posizioni di SafeGraph
Tasty Bytes gestisce food truck in molte città di tutto il mondo e ogni food truck può scegliere due posizioni di vendita al giorno. Le posizioni corrispondono a punti di interesse di SafeGraph. Il tuo scopo è unire latitudine e longitudine nei dati Marketplace di SafeGraph con i tuoi dati sulle vendite per turno per utilizzarli come caratteristiche nell'addestramento dei modelli.
Passaggio 1 - Acquisire dal Marketplace Snowflake i dati sui punti di interesse di SafeGraph
- Accedi al tuo account Snowflake.
- Segui i passaggi e il video riportati sotto per accedere ai dati SafeGraph nel Marketplace dal tuo account Snowflake.
- Fai clic su -> Icona Home
- Fai clic su -> Marketplace
- Cerca -> frostbyte
- Fai clic su -> SafeGraph: frostbyte
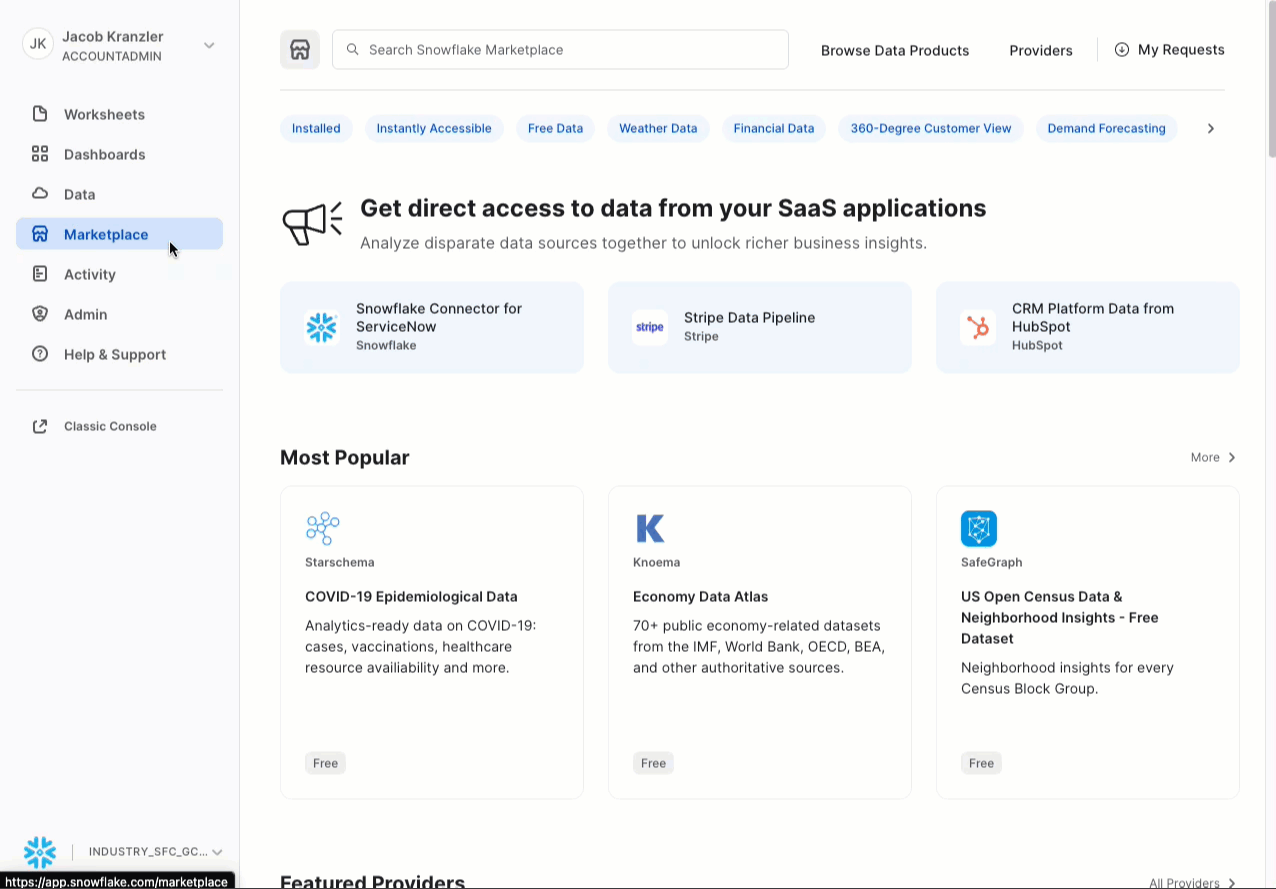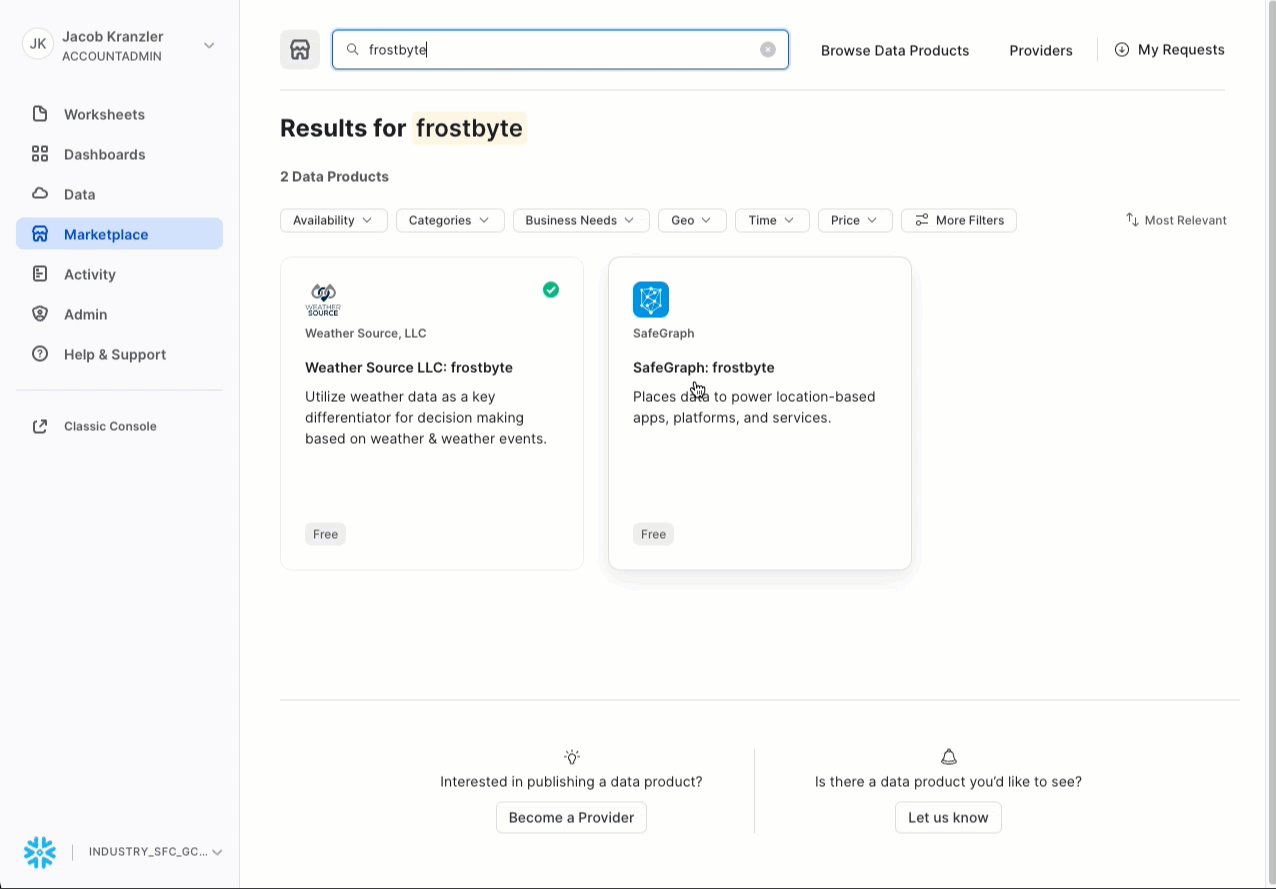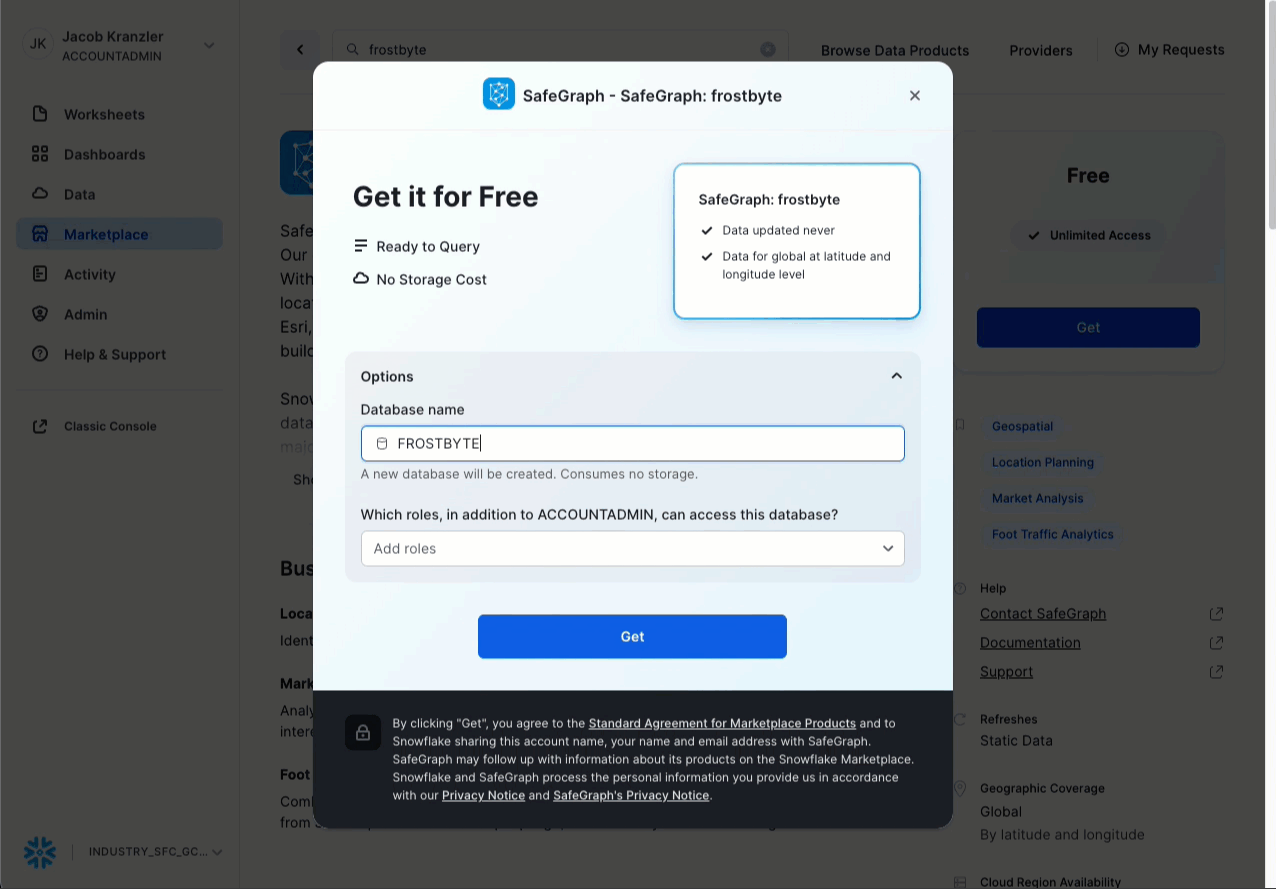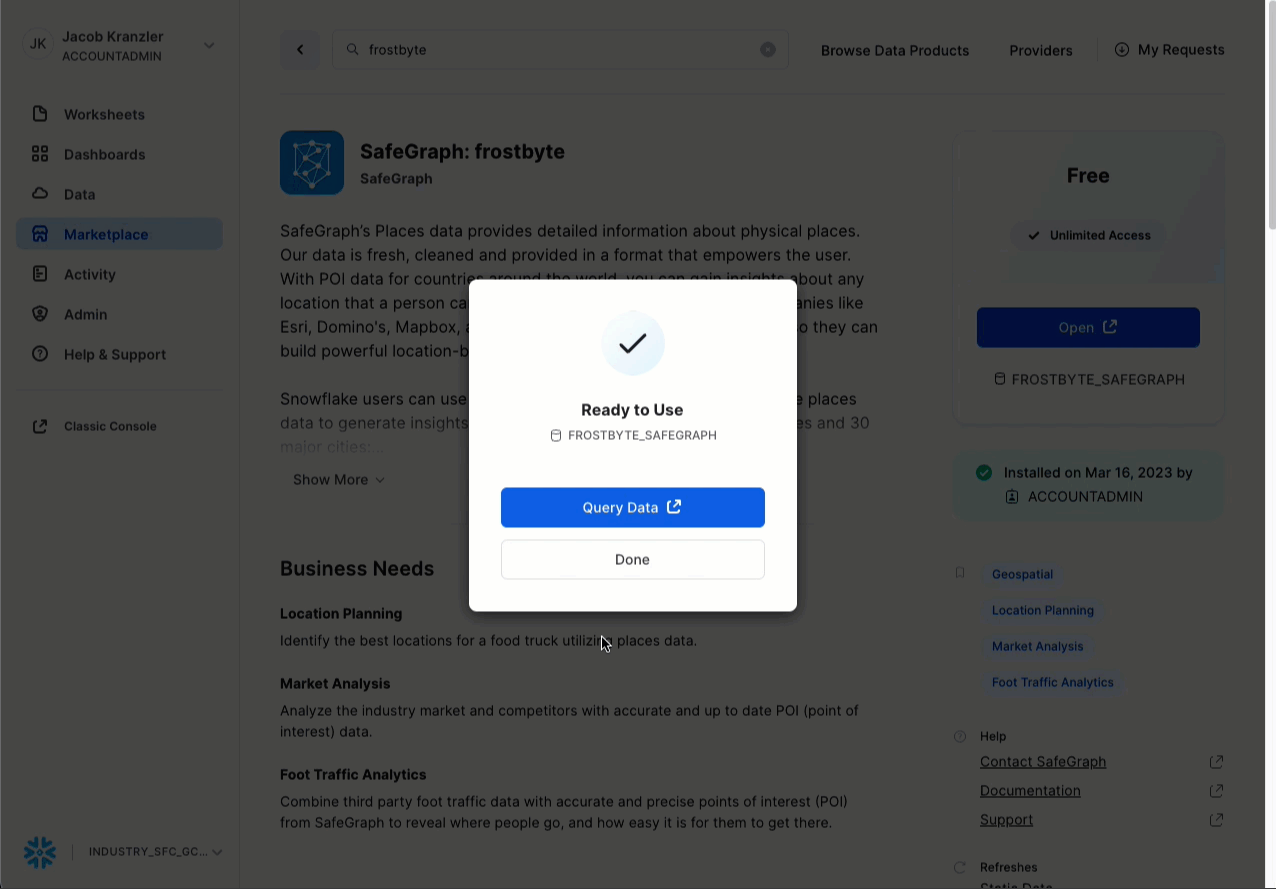
- Fai clic su -> Get
- Rinomina il database -> FROSTBYTE_SAFEGRAPH (tutte maiuscole)
- Consenti l'accesso ad altri ruoli -> PUBLIC
Passaggio 2 - Creare oggetti, caricare i dati e unire i dati
Vai a Worksheets, fai clic su "+" nell'angolo superiore destro per creare un nuovo foglio di lavoro e scegli "SQL Worksheet".
Incolla ed esegui il seguente codice SQL nel foglio di lavoro per creare oggetti Snowflake (warehouse, database, schema), caricare i dati degli ordini grezzi da S3 e modellarli per l'uso a valle.
-- use our accountadmin role
USE ROLE accountadmin;
-- create a development database for data science work
CREATE OR REPLACE DATABASE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app;
-- create raw, harmonized, and analytics schemas
-- raw zone for data ingestion
CREATE OR REPLACE SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.raw;
-- harmonized zone for data processing
CREATE OR REPLACE SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.harmonized;
-- analytics zone for development
CREATE OR REPLACE SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics;
-- create csv file format
CREATE OR REPLACE FILE FORMAT frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.raw.csv_ff
type = 'csv';
-- create an external stage pointing to S3
CREATE OR REPLACE STAGE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.raw.s3load
COMMENT = 'Quickstarts S3 Stage Connection' url = 's3://sfquickstarts/frostbyte_tastybytes/'
file_format = frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.raw.csv_ff;
-- define shift sales table
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.raw.shift_sales(
location_id NUMBER(19,0),
city VARCHAR(16777216),
date DATE,
shift_sales FLOAT,
shift VARCHAR(2),
month NUMBER(2,0),
day_of_week NUMBER(2,0),
city_population NUMBER(38,0)
);
-- create and use a compute warehouse
CREATE OR REPLACE WAREHOUSE tasty_ml_app_wh AUTO_SUSPEND = 60;
USE WAREHOUSE tasty_ml_app_wh;
-- ingest from S3 into the shift sales table
COPY INTO frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.raw.shift_sales
FROM @frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.raw.s3load/analytics/shift_sales/;
-- join in SafeGraph data
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.harmonized.shift_sales
AS
SELECT
a.location_id,
a.city,
a.date,
a.shift_sales,
a.shift,
a.month,
a.day_of_week,
a.city_population,
b.latitude,
b.longitude,
b.location_name,
b.street_address
FROM frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.raw.shift_sales a
JOIN frostbyte_safegraph.public.frostbyte_tb_safegraph_s b
ON a.location_id = b.location_id;
-- promote the harmonized table to the analytics layer for data science development
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics.shift_sales_v
AS
SELECT * FROM frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.harmonized.shift_sales;
-- view shift sales data
SELECT * FROM frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics.shift_sales_v;
Per garantire l'efficacia delle misure di sicurezza, è essenziale stabilire un account utente dedicato per l'applicazione, separato dal tuo account personale. Questo nuovo account verrà utilizzato per interrogare Snowflake. Secondo le best practice di sicurezza, l'account utilizzerà l'autenticazione a coppia di chiavi e avrà un accesso limitato all'interno dell'ambiente Snowflake.
Passaggio 1 - Generare la chiave pubblica e privata per l'autenticazione
Esegui i seguenti comandi per creare una chiave pubblica e una chiave privata. Queste chiavi sono necessarie per autenticare l'utente in Snowflake.
$ cd ~/.ssh
$ openssl genrsa -out snowflake_app_key 4096
$ openssl rsa -in snowflake_app_key -pubout -out snowflake_app_key.pub
Passaggio 2 - Creare l'utente e il ruolo in Snowflake e concedere l'accesso ai dati a questo nuovo ruolo
Esegui le seguenti istruzioni SQL per creare l'account utente e concedere l'accesso ai dati necessari per l'applicazione.
-- use our securityadmin role
USE ROkLE securityadmin;
-- create our tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo role
CREATE ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
-- use our accountadmin role
USE ROLE accountadmin;
-- grant privileges to our tasty_bytes_data_app_demo role
GRANT USAGE ON WAREHOUSE tasty_ml_app_wh TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.harmonized TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.raw TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL VIEWS IN SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL VIEWS IN SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.harmonized TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.harmonized TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.raw TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
-- use our useradmin role
USE ROLE useradmin;
-- Open the ~/.ssh/snowflake_app_key.pub file from Step 1 and copy the contents starting just after the PUBLIC KEY header,
-- and stopping just before the PUBLIC KEY footer for INSERT_RSA_PUBLIC_KEY_HERE.
CREATE USER data_ml_app_demo
RSA_PUBLIC_KEY='<INSERT_RSA_PUBLIC_KEY_HERE>'
DEFAULT_ROLE=tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo
DEFAULT_WAREHOUSE=tasty_ml_app_wh
MUST_CHANGE_PASSWORD=FALSE;
-- use our securityadmin role
USE ROLE securityadmin;
GRANT ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo TO USER data_ml_app_demo;
Panoramica
Tasty Bytes intende ottenere una crescita annuale delle vendite del 25% per cinque anni. Per supportare questo obiettivo e massimizzare i ricavi giornalieri in tutta la flotta di food truck, il team di data science deve creare un modello ML per portare i food truck nelle posizioni in cui sono previste le vendite più elevate per un dato turno.
Vai a Worksheets, fai clic su "+" nell'angolo superiore destro per creare un nuovo foglio di lavoro e scegli "SQL Worksheet".
Incolla ed esegui il seguente codice SQL nel foglio di lavoro per addestrare e distribuire il modello per produrre suggerimenti sulle posizioni.
USE ROLE accountadmin;
USE DATABASE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app;
USE SCHEMA analytics;
USE WAREHOUSE tasty_ml_app_wh;
CREATE STAGE IF NOT EXISTS app_stage;
-- Create stored proc for shift table
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE build_shift_feature_table()
RETURNS string
LANGUAGE python
RUNTIME_VERSION = '3.8'
PACKAGES = ('snowflake-snowpark-python')
HANDLER = 'create_table'
AS
$$
def create_table(session):
import snowflake.snowpark.functions as F
import snowflake.snowpark.types as T
from snowflake.snowpark import Window
# Create DataFrame
snowpark_df = session.table("frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics.shift_sales_v")
# Create rolling average
window_by_location_all_days = (
Window.partition_by("location_id", "shift")
.order_by("date")
.rows_between(Window.UNBOUNDED_PRECEDING, Window.CURRENT_ROW - 1))
snowpark_df = snowpark_df.with_column(
"avg_location_shift_sales",
F.avg("shift_sales").over(window_by_location_all_days))
# Impute
snowpark_df = snowpark_df.fillna(value=0, subset=["avg_location_shift_sales"])
# Encode
snowpark_df = snowpark_df.with_column("shift", F.iff(F.col("shift") == "AM", 1, 0))
# Get date
date_tomorrow = snowpark_df.filter(F.col("shift_sales").is_null()).select(F.min("date")).collect()[0][0]
# Filter
feature_df = snowpark_df.filter(F.col("date") == date_tomorrow).drop(F.col("shift_sales"))
# Get Location Detail
location_df = session.table("frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics.shift_sales_v").select("location_id", "location_name", "street_address")
# Join
feature_df = feature_df.join(location_df,
feature_df.location_id == location_df.location_id,
"left") \
.drop(location_df.location_id) \
.drop(location_df.location_name) \
.drop(location_df.street_address) \
.rename(feature_df.location_id, "location_id") \
.rename(feature_df.location_name, "location_name") \
.rename(feature_df.street_address, "street_address")
# Save table
feature_df.write.mode("overwrite").save_as_table("frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics.shift_features")
return "SUCCESS"
$$;
-- Call sproc to create feature table
Call build_shift_feature_table();
-- Set permissions
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON TABLE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics.shift_features to tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
-- Create training stored procedure
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE SPROC_TRAIN_LINREG()
RETURNS
STRING LANGUAGE
PYTHON RUNTIME_VERSION = '3.8'
PACKAGES = ('snowflake-snowpark-python','scikit-learn','joblib')
HANDLER = 'train_model'
AS
$$
def train_model(session):
import snowflake.snowpark.functions as F
import snowflake.snowpark.types as T
from snowflake.snowpark import Window
# Create DataFrame
snowpark_df = session.table("frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app.analytics.shift_sales_v")
# Create rolling average
window_by_location_all_days = (
Window.partition_by("location_id", "shift")
.order_by("date")
.rows_between(Window.UNBOUNDED_PRECEDING, Window.CURRENT_ROW - 1))
snowpark_df = snowpark_df.with_column(
"avg_location_shift_sales",
F.avg("shift_sales").over(window_by_location_all_days))
# Impute
snowpark_df = snowpark_df.fillna(value=0, subset=["avg_location_shift_sales"])
# Encode
snowpark_df = snowpark_df.with_column("shift", F.iff(F.col("shift") == "AM", 1, 0))
# Get date
date_tomorrow = snowpark_df.filter(F.col("shift_sales").is_null()).select(F.min("date")).collect()[0][0]
# Filter to historical
historical_snowpark_df = snowpark_df.filter(F.col("shift_sales").is_not_null())
# Drop
historical_snowpark_df = historical_snowpark_df.drop("location_id", "city", "date")
# Split
train_snowpark_df, test_snowpark_df = historical_snowpark_df.randomSplit([0.8, 0.2])
# Import packages
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from joblib import dump
feature_cols = ["MONTH", "DAY_OF_WEEK", "LATITUDE", "LONGITUDE", "CITY_POPULATION", "AVG_LOCATION_SHIFT_SALES", "SHIFT"]
target_col = "SHIFT_SALES"
# Get training data
df = train_snowpark_df.to_pandas()
# Set inputs X and outputs y
X = df[feature_cols]
y = df[target_col]
# Train model
model = LinearRegression().fit(X, y)
# Save model
model_name = "linreg_location_sales_model.sav"
dump(model, "/tmp/" + model_name)
session.file.put(
"/tmp/" + model_name,
"@APP_STAGE",
auto_compress=False,
overwrite=True
)
return "SUCCESS"
$$;
-- Train model
Call sproc_train_linreg();
-- Deploy the model as a UDF
CREATE OR REPLACE
FUNCTION udf_predict_location_sales_prod(arg1 FLOAT,arg2 FLOAT,
arg3 FLOAT,arg4 FLOAT,
arg5 FLOAT,arg6 FLOAT, arg7 FLOAT)
RETURNS FLOAT
LANGUAGE PYTHON
RUNTIME_VERSION=3.8
IMPORTS=('@APP_STAGE/linreg_location_sales_model.sav')
PACKAGES=('scikit-learn','joblib','cloudpickle==2.0.0','pandas', 'cachetools') HANDLER='predict'
as
$$
import pandas
import cachetools
from _snowflake import vectorized
@cachetools.cached(cache={})
def load_model(filename):
import joblib
import sys
import os
import_dir = sys._xoptions.get("snowflake_import_directory")
if import_dir:
with open(os.path.join(import_dir, filename), 'rb') as file:
m = joblib.load(file)
return m
@vectorized(input=pandas.DataFrame)
def predict(X: pandas.DataFrame) -> pandas.Series:
# Load the model
model = load_model("linreg_location_sales_model.sav")
# Get predictions
predictions = model.predict(X)
# Return rounded predictions
return predictions.round(2)
$$;
-- Set permissions
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON FUNCTION udf_predict_location_sales_prod(FLOAT,FLOAT,FLOAT, FLOAT,FLOAT,FLOAT,FLOAT) to tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
L'applicazione che eseguirai è scritta in React Native.
Passaggio 1 - Ottenere il codice sorgente
- Clona il repository utilizzando
https://github.com/sf-gh-sjasti/IntegrationTastyBytesMLModelInDataApp.git reactNativeMLApp - Vai alla cartella
cd reactNativeMLApp - Esegui
npm installper installare le dipendenze
Passaggio 2 - Configurare l'applicazione
- Apri la cartella
reactNativeMLAppin VS Code o nel tuo IDE preferito. - Apri il file
.enve aggiorna il valorePRIVATE_KEYcon la chiave privata. Copia e incolla l'intera chiave privata da~/.ssh/snowflake_app_key.pub, compresa l'intestazione (-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----) e il piè di pagina (-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----). - Se ti trovi nella regione US-West, aggiorna
SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT_IDENTIFIERcon il tuo account Snowflake oppure, se non ti trovi nella regione US-West, aggiornaSNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT_IDENTIFIERcon ‘.'. Per recuperare il valore snowflake_account da Snowflake, eseguiSELECT CURRENT_ACCOUNT()in Snowsight. Per recuperare il valore della regione da Snowflake, eseguiSELECT CURRENT_REGION()in Snowsight. Per la regione US-West, SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT_IDENTIFIER e SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT sono uguali. - Aggiorna
SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNTcon il tuo account Snowflake. - Aggiorna
PUBLIC_KEY_FINGERPRINTcon l'impronta digitale della tua chiave pubblica. Per ottenere l'impronta digitale della chiave pubblica, esegui il seguente codice SQL in SnowsightDESCRIBE USER data_app_demoe recupera il valore della proprietà RSA_PUBLIC_KEY_FP.
Passaggio 3 - Esaminare il codice sorgente
Stiamo utilizzando l'autenticazione a coppia di chiavi per eseguire l'autenticazione in Snowflake tramite la SQL API. Per capire come viene generato il token JWT, puoi fare riferimento a Tokens.js. Locations.js contiene il codice sorgente per il rendering della schermata Locations. Puoi anche fare riferimento a questo file per scoprire come interrogare un'UDF utilizzando la SQL API, comprese le intestazioni necessarie.
Passaggio 4 - Testare l'applicazione
- Esegui
npx expo start --cleare premi il tastowper eseguire l'applicazione in un browser web - L'applicazione viene avviata in un browser web
- All'avvio viene visualizzata la schermata degli ordini in coda,
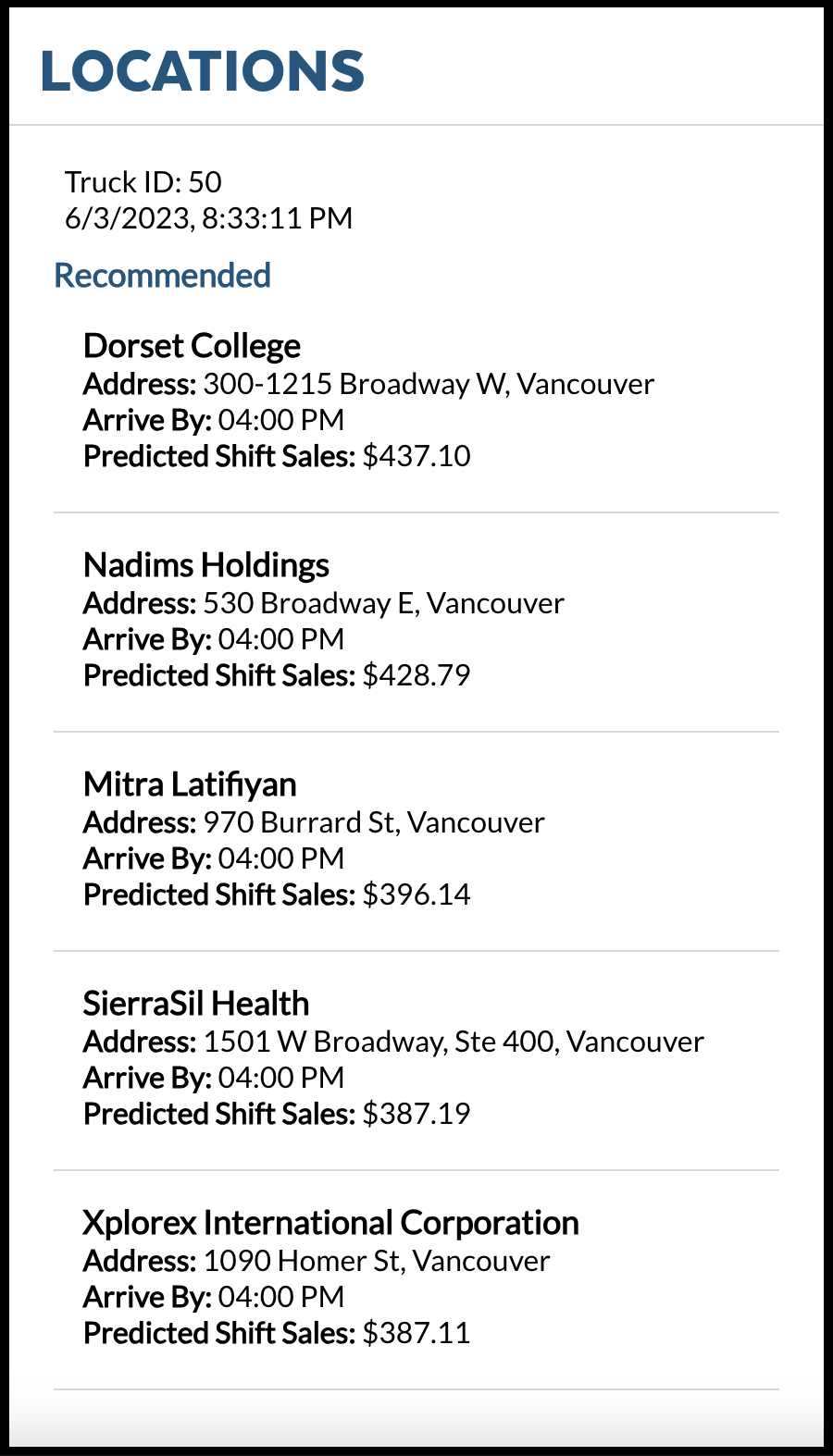
Vai a Snowsight Worksheets, fai clic su "+" nell'angolo superiore destro per creare un nuovo foglio di lavoro e scegli "SQL Worksheet". Incolla ed esegui il seguente codice SQL nel foglio di lavoro per eliminare gli oggetti Snowflake creati in questo quickstart.
USE ROLE accountadmin;
DROP DATABASE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_ml_app;
DROP WAREHOUSE tasty_ml_app_wh;
USE ROLE securityadmin;
DROP USER data_ml_app_demo;
DROP ROLE tasty_bytes_data_ml_app_demo;
Conclusione
Ce l'hai fatta! Hai completato il quickstart Integrare un modello ML per i suggerimenti sulle posizioni di Tasty Bytes in una data application React Native.
Completando questo quickstart hai:
- Acquisito dati di terze parti dal Marketplace Snowflake
- Addestrato un modello ML in Snowflake con una stored procedure
- Distribuito il modello ML come UDF in Snowflake per l'inferenza del modello
- Integrato il modello ML nella data application
Fasi successive
Per saperne di più sul modello ML per i suggerimenti sulle posizioni, fai riferimento al nostro quickstart Tasty Bytes - Introduzione a Snowpark per la data science.
Per continuare il tuo percorso nel Data Cloud di Snowflake, visita il link riportato sotto per vedere gli altri quickstart Powered by Tasty Bytes disponibili.