Getting started with AI on enterprise data can seem overwhelming. Between getting familiar with LLMs, how to perform custom prompt engineering, fine-tuning an existing foundation model and how to get a wide range of LLMs deployed/integrated to run multiple tests all while keeping that valuable enterprise data secure. Well, a lot of these complexities are being abstracted away for you in Snowflake Cortex AI.
What is Snowflake Cortex?
Snowflake Cortex is an intelligent, fully managed service that provides access to industry-leading large language models (LLMs) and chat with your data services.. Cortex AI capabilities include:
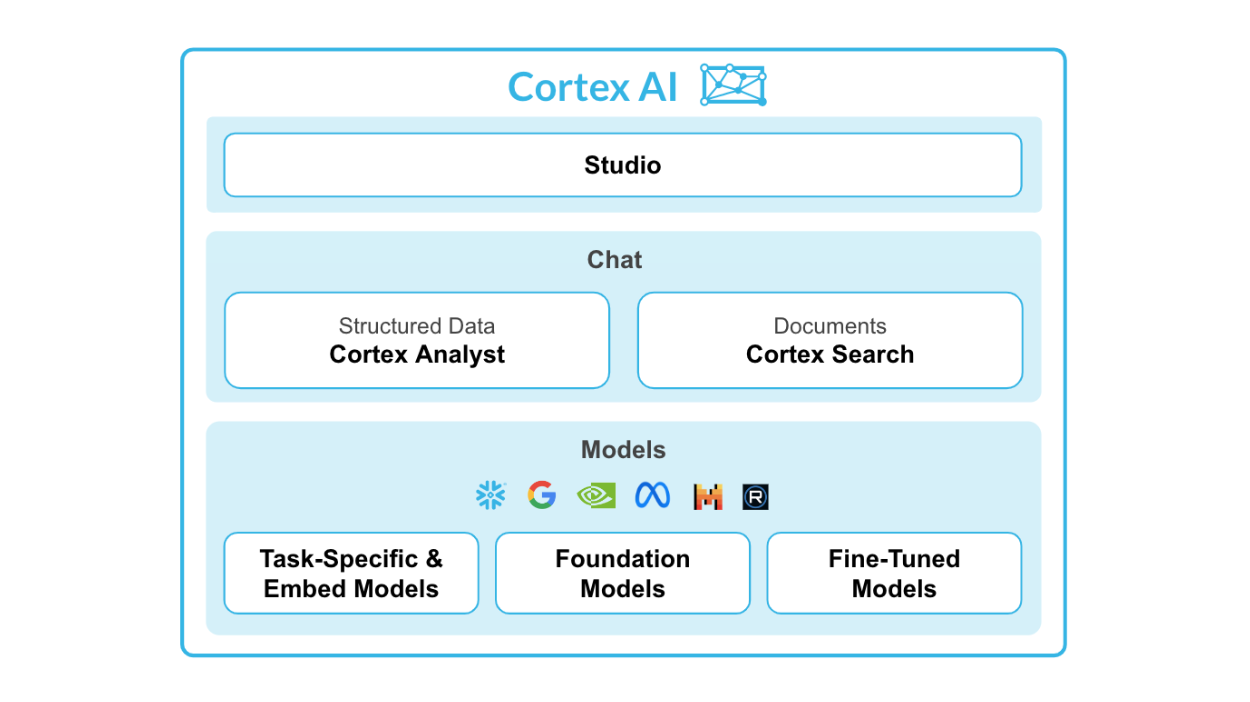
Models: Access to tasks specific functions such as sentiment analysis, translation as well as Foundation Models from Snowflake, Meta, Mistral AI. Leading models from Meta and Mistral AI are available for serverless fine-tuning (public preview).
Chat Services: Ask questions against unstructured data, such as documents using Cortex Search or ask questions to structured data, such as sales transactions using Cortex Analyst - both coming soon to public preview.
AI & ML Studio: This a no-code development workspace in Snowflake. Specifically for LLMs, Studio lets users quickly try out models, easily fine-tune models, and set up use cases such as search so you can expedite delivery of applications.
In this quickstart, we will go through 2 flows – Use Cortex AI to fine-tune an LLM to categorize customer support tickets for a Telecom provider, and generate custom email/text communications tailored to each customer ticket.
Learn more about Snowflake Cortex.
Fine-tuning for Enterprise Use-cases
Compared to a smaller size model such as Mistral 7B, a foundation large language model such as mistral-large can be used to categorize support tickets with higher accuracy. But using a large language model comes with higher inference costs.
Using fine-tuning, organizations can make smaller models really good at specific tasks to deliver results with the accuracy of larger models at just a fraction of the cost.
What You Will Learn
By the end of this quickstart guide, you will be able to use Snowflake Cortex AI to: Categorize: Use LLM to categorize support tickets Generate: Prepare training dataset for fine-tuning by leveraging an LLM for annotations Fine-tune: Use smaller, fine-tune model to achieve accuracy of larger model at fraction of cost Generate: Custom email/text communications tailored to each support ticket
Prerequisites
- A Snowflake account in a region where Snowflake Cortex is available. Check availability.
- A Snowflake user created with ACCOUNTADMIN permissions. This user will be used to get things setup in Snowflake.
- A GitHub account. If you don't already have a GitHub account you can create one for free. Visit the Join GitHub page to get started.
- Download the Snowflake Notebook from this Git repository for fine-tuning the model.
Load the Demo Notebook
A Snowflake Notebook with the required code snippets for this quickstart are available in this repository.
To load the demo notebook into your Snowflake account, follow these steps:
- Download the file by clicking on the
Download raw filefrom the top right. - Go to the Snowflake web interface, Snowsight, on your browser.
- Navigate to
Project>Notebooksfrom the left menu bar. - Import the
.ipynbfile you've downloaded into your Snowflake Notebook by using theImport from .ipynbbutton located on the top right of the Notebooks page.
Create Table and Load Data
Run these SQL statements in a SQL worksheet to create support_tickets table and load data.
CREATE or REPLACE file format csvformat
SKIP_HEADER = 1
FIELD_OPTIONALLY_ENCLOSED_BY = '"'
type = 'CSV';
CREATE or REPLACE stage support_tickets_data_stage
file_format = csvformat
url = 's3://sfquickstarts/finetuning_llm_using_snowflake_cortex_ai/';
CREATE or REPLACE TABLE SUPPORT_TICKETS (
ticket_id VARCHAR(60),
customer_name VARCHAR(60),
customer_email VARCHAR(60),
service_type VARCHAR(60),
request VARCHAR,
contact_preference VARCHAR(60)
)
COMMENT = '{"origin":"sf_sit-is", "name":"aiml_notebooks_fine_tuning", "version":{"major":1, "minor":0}, "attributes":{"is_quickstart":1, "source":"sql"}}';
COPY into SUPPORT_TICKETS
from @support_tickets_data_stage;
Support Ticket Categorization using Cortex AI
First, let's use Snowflake Cortex COMPLETE() to categorize the support tickets into different buckets – Roaming Fees, Slow data speed, Add new line, Closing account and more.
We can use any Cortex supported model under the hood to invoke the COMPLETE() function. In this quickstart, let's use mistral-large and use the following prompt.
prompt = """You are an agent that helps organize requests that come to our support team.
The request category is the reason why the customer reached out. These are the possible types of request categories:
Roaming fees
Slow data speed
Lost phone
Add new line
Closing account
Try doing it for this request and return only the request category only.
"""
Using a powerful and large language model such as mistral-large might be highly accurate without doing any complex customizations but running mistral-large on millions of support tickets comes with a cost. So, let's try the same COMPLETE() function with the same prompt but this time with a smaller model such as mistral-7b.
As we can see, the smaller model mistral-7b does not generate results with a consistent structure.
To overcome this, we could fine-tune mistral-7b particularly for this task. This fine-tuned model will be smaller in size and the inference cost is only a fraction of what a larger model would cost.
Fine-tuning
To fine-tune the language model, we need training data that includes support ticket requests and right category labels for each of them. Annotations for millions of support tickets are not readily available. So we could leverage an existing large language model to create category labels and prepare the dataset for fine-tuning.
Next step is to split the curated dataset into a training and a test set. There are two ways you can fine-tune a large language model.
- Use Snowflake Cortex AI Studio that allows you to run fine-tuning from the UI. This is currently in PrPr
- Use FINETUNE() Cortex function to run the fine-tune job using SQL queries. This is currently available in PuPr.
Fine-tuning using Cortex AI Studio
Once we have the training data, we could use Snowflake Cortex AI Studio to fine-tune. Cortex AI features a no-code fine-tuning from the UI using the Create Custom LLM option.
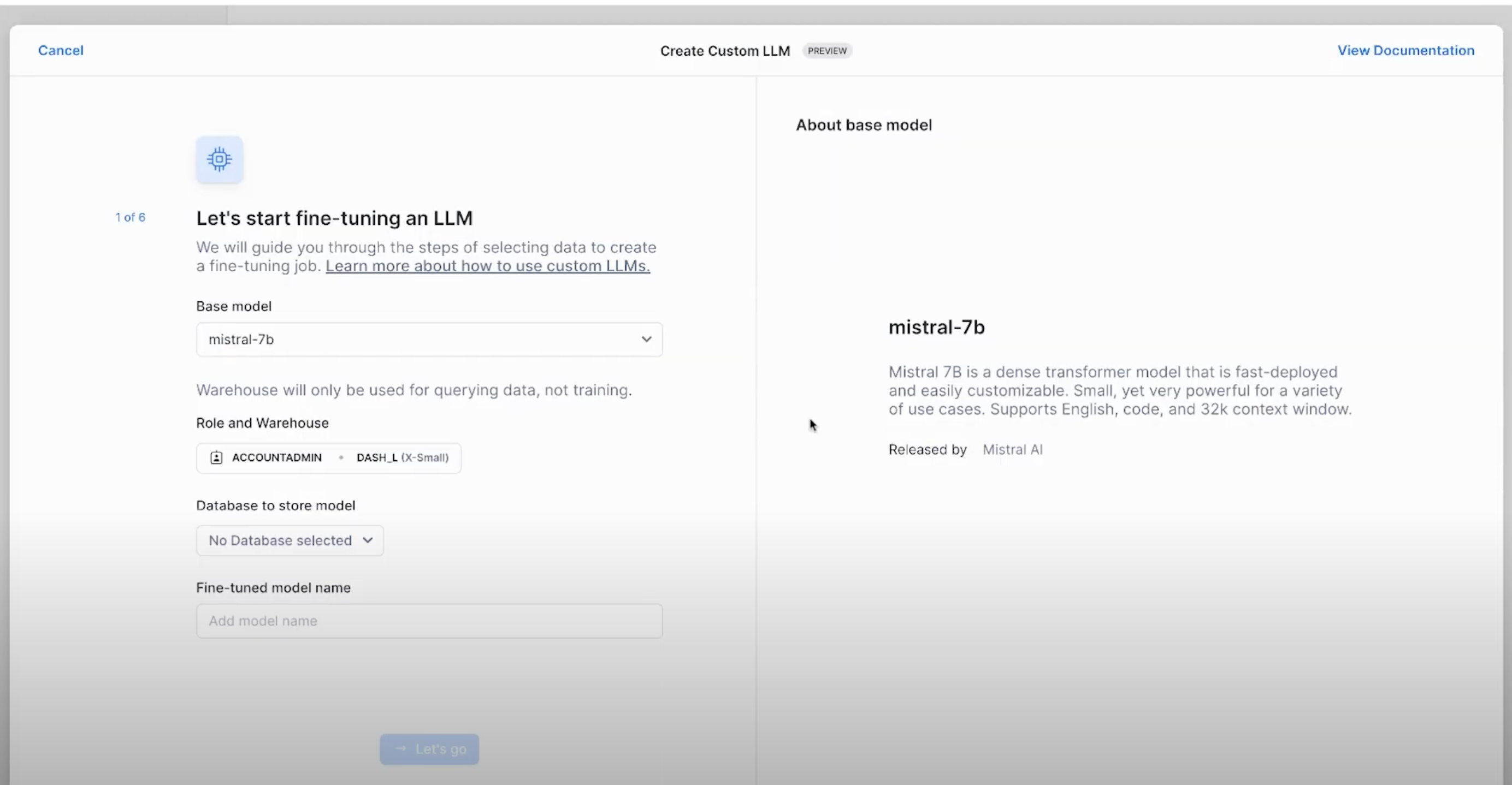
- In the wizard that appears, select the base model for fine-tuning. In this case,
mistral-7b. - Select the appropriate role and warehouse for model fine-tuning.
- Select the right database to store the fine-tuned model as well.
- Select the training data including the prompt column, and complete column
- In the end, select the validation data for Cortex to evaluate the fine-tuning process too
- Inferencing the fine-tuned model
Fine-tuning using FINETUNE() SQL API
Alternatively, you can also fine-tune the LLM using SQL API FINETUNE(). Learn more about the syntax here.
select snowflake.cortex.finetune(
'CREATE',
'CORTEX_FINETUNING_DB.PUBLIC.SUPPORT_TICKETS_FINETUNED_MISTRAL_7B', 'mistral-7b',
'SELECT prompt, mistral_large_response as completion from CORTEX_FINETUNING_DB.PUBLIC.support_tickets_train',
'SELECT prompt, mistral_large_response as completion from CORTEX_FINETUNING_DB.PUBLIC.support_tickets_eval'
);
After running the above query, we can keep track of the fine-tuning job using the below command.
select snowflake.cortex.finetune('DESCRIBE', 'CortexFineTuningWorkflow_f4016e33-92ce-45d3-918a-19115c398f10');
Inferencing the fine-tuned model
Once the fine-tuning is complete, we could run inference on the model by simply invoking the Cortex AI COMPLETE() with the fine-tuned model name as one of the parameters.
fine_tuned_model_name = 'SUPPORT_TICKETS_FINETUNED_MISTRAL_7B'
sql = f"""select ticket_id, request,
trim(snowflake.cortex.complete('{fine_tuned_model_name}',concat('{prompt}',request)),'\n') as fine_tuned_mistral_7b_model_response
from support_tickets"""
df_fine_tuned_mistral_7b_response = session.sql(sql)
df_fine_tuned_mistral_7b_response
Automated Generation of Email Responses to support tickets using LLMs
After categorizing the support tickets into different categories based on the reason for the support request, we can also use Cortex AI to auto-generate the email/text responses to these support requests.
The following code snippet creates a nimble steamlit application in a Snowflake Notebook that you can use to iterate through the different prompts while invoking the Complete() function.
st.subheader("Auto-generate custom emails or text messages")
with st.container():
with st.expander("Edit prompt and select LLM", expanded=True):
entered_prompt = st.text_area('Prompt',"""Please write an email or text promoting a new plan that will save customers total costs. If the customer requested to be contacted by text message, write text message response in less than 25 words, otherwise write email response in maximum 100 words.""")
with st.container():
left_col,right_col = st.columns(2)
with left_col:
selected_category = st.selectbox('Select category',('Roaming fees', 'Closing account', 'Add new line', 'Slow data speed'))
with right_col:
selected_llm = st.selectbox('Select LLM',('snowflake-arctic','llama3-8b','mistral-large', 'reka-flash',))
with st.container():
_,mid_col,_ = st.columns([.4,.3,.3])
with mid_col:
generate_template = st.button('Generate messages ⚡',type="primary")
with st.container():
if generate_template:
sql = f"""select s.ticket_id, s.customer_name, concat(IFF(s.contact_preference = 'Email', '📩', '📲'), ' ', s.contact_preference) as contact_preference, snowflake.cortex.complete('{selected_llm}',
concat('{entered_prompt}','Here is the customer information: Name: ',customer_name,', Contact preference: ', contact_preference))
as llm_response from support_tickets as s join support_tickets_train as t on s.ticket_id = t.ticket_id
where t.mistral_large_response = '{selected_category}' limit 10"""
with st.status("In progress...") as status:
df_llm_response = session.sql(sql).to_pandas()
st.subheader("LLM-generated emails and text messages")
for row in df_llm_response.itertuples():
status.caption(f"Ticket ID: `{row.TICKET_ID}`")
status.caption(f"To: {row.CUSTOMER_NAME}")
status.caption(f"Contact through: {row.CONTACT_PREFERENCE}")
status.markdown(row.LLM_RESPONSE.replace("--", ""))
status.divider()
status.update(label="Done!", state="complete", expanded=True)
Depending on the values in the contact_preference column, Cortex AI can generate text or email messages that can be used for customer support responses.
Congratulations! You've successfully completed the Cortex Fine-tuning Quickstart Guide. You can use any of these supported LLMs for fine-tuning with Cortex.
What You Learned
You have learnt how to use Snowflake Cortex AI to: Categorize: Use LLM to categorize support tickets Generate: Prepare training dataset for fine-tuning by leveraging an LLM for annotations Fine-tune: Use smaller, fine-tune model to achieve accuracy of larger model at fraction of cost Generate: Custom email/text communications tailored to each support ticket