
Tasty Bytes is a fictional global food truck enterprise that has established its presence in 30 cities spanning across 15 countries, boasting a network of 450 trucks offering 15 diverse menu types under various brands. Catering to the needs of both customers and truck owners/operators, Tasty Bytes has developed a robust Truck Driver App. This specialized app provides truck owners/operators with a comprehensive 360-degree view of the order process, allowing them to efficiently manage their operations. Once orders are placed by customers, they are queued for processing, and drivers have the flexibility to prioritize each order based on various factors. This driver-focused app grants efficient access to both historical and real-time order data, enabling swift updates on ongoing orders. However, the exponential rise in daily order volumes, driven by Tasty Bytes growing success, has strained the application's performance and its ability to support concurrent users effectively.
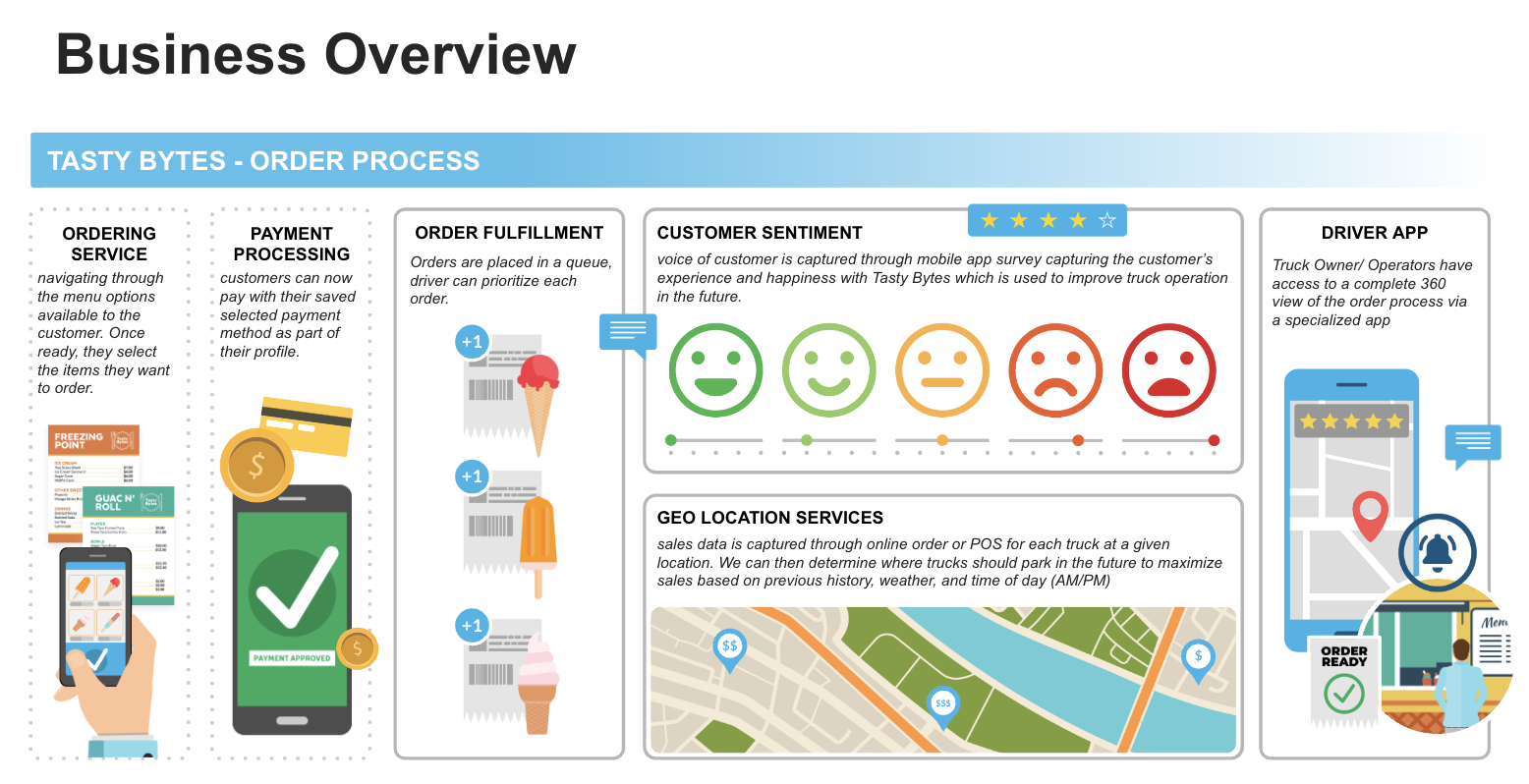
To tackle scaling challenges, the implementation of Hybrid Tables within this lightweight transactional application aims to harness several advantages. These tables provide quicker lookups for current and past orders, essential for driver efficiency. Supporting ACID transactions with row locking, they simplify the process of updating order statuses, ensuring data integrity and reliability. Moreover, Hybrid Tables facilitate seamless integration with Snowflake's existing business data, allowing for robust analytics. This blend of features enhances overall performance, scalability, and flexibility, making Hybrid Tables the ideal solution for addressing the evolving needs of Tasty Bytes food truck network.
Prerequisites
- Snowflake non-trail account with Hybrid Tables enabled
- Privileges necessary to create a user, database, and warehouse in Snowflake
- Ability to install and run software on your computer
- Basic experience using git
- Intermediate knowledge of SQL
- Access to run SQL in the Snowflake
- Understanding of Application Workflow
What You'll Learn
- How to develop Data Applications leveraging Snowflake Hybrid Tables
- Authenticating with Snowflake using Key Pair Authentication
- Leveraging SQLAlchemy to connect to Snowflake from the Application
- Developing Flask API's
- Developing React Native Application
What You'll Need
What You'll Build
- A React Native Data Applcation Leveraging Hybrid Tables
For this demo, we are utilizing Tasty Bytes Orders data to develop an application tailored for truck drivers, leveraging Snowflake hybrid tables. Here are the advantages of using Snowflake hybrid tables for this purpose:
- Efficient Data Access: Snowflake hybrid tables offer faster lookups for current and past orders, ensuring that truck drivers can quickly access the orders in their queue without delays.
- Real-time Updates: With Snowflake hybrid tables, truck drivers can promptly update the status of orders once they are ready for completion. This real-time update capability enhances the efficiency of order management and ensures timely delivery to customers.
- Seamless Integration: Snowflake hybrid tables enable seamless integration with the application, allowing truck drivers to view completed orders effortlessly. This integration streamlines the process of accessing historical order data, facilitating better decision-making and analysis.
By leveraging Snowflake hybrid tables, the application provides truck drivers with enhanced capabilities, including the ability to view orders in their queue, update order statuses in real-time, and access completed orders seamlessly. This ensures smoother operations and improved efficiency in managing Tasty Bytes food truck network.
You will use Snowsight, the Snowflake web interface, to:
- Create Snowflake objects (warehouse, database, schema)
- Create hybrid tables needed for the application
- Ingest data from S3
Creating Objects, Loading Data, and Accessing Data
- Navigate to Worksheets
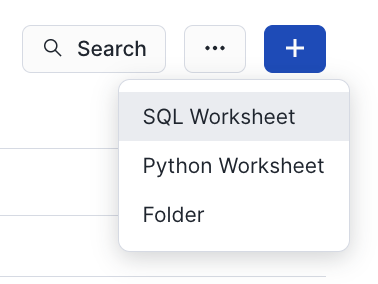
- click "+" in the top-right corner to create a new Worksheet, and choose "SQL Worksheet".
Paste and run the following SQL in the worksheet to create Snowflake objects (warehouse, database, schema), ingest raw orders data from S3.
-- use our accountadmin role
USE ROLE accountadmin;
-- create our database
CREATE OR REPLACE DATABASE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore;
-- create RAW zone for data ingestion
CREATE OR REPLACE SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw;
-- create CSV file format
CREATE OR REPLACE FILE FORMAT frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.csv_unistore_ff
type = 'csv';
-- create an external stage pointing to S3
CREATE OR REPLACE STAGE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.s3load_unistore
COMMENT = 'Quickstarts S3 Stage Connection for Unistore'
url = 's3://sfquickstarts/frostbyte_tastybytes/unistore'
file_format = frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.csv_unistore_ff;
-- create CUSTOMER_LOYALTY HYBRID table which holds customer information
create or replace HYBRID TABLE FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.CUSTOMER_LOYALTY (
CUSTOMER_ID NUMBER(38,0) NOT NULL,
FIRST_NAME VARCHAR(16777216),
LAST_NAME VARCHAR(16777216),
CITY VARCHAR(16777216),
COUNTRY VARCHAR(16777216),
POSTAL_CODE VARCHAR(16777216),
PREFERRED_LANGUAGE VARCHAR(16777216),
GENDER VARCHAR(16777216),
FAVOURITE_BRAND VARCHAR(16777216),
MARITAL_STATUS VARCHAR(16777216),
CHILDREN_COUNT VARCHAR(16777216),
SIGN_UP_DATE DATE,
BIRTHDAY_DATE DATE,
E_MAIL VARCHAR(16777216),
PHONE_NUMBER VARCHAR(16777216),
primary key (CUSTOMER_ID) rely
)
COMMENT = '{"origin":"sf_sit-is", "name":"tb_unistore", "version":{"major":1, "minor":0}, "attributes":{"is_quickstart":1, "source":"react"}}';
-- create MENU_TYPE HYBRID table which holds menu details
create or replace HYBRID TABLE FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.MENU_TYPE (
MENU_TYPE_ID NUMBER(38,0) NOT NULL,
MENU_TYPE VARCHAR(16777216),
primary key (MENU_TYPE_ID) rely
);
-- create MENU HYBRID table which holds menu details
create or replace HYBRID TABLE FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.MENU (
MENU_ID NUMBER(19,0) NOT NULL,
MENU_TYPE_ID NUMBER(38,0) NOT NULL,
TRUCK_BRAND_NAME VARCHAR(16777216),
MENU_ITEM_ID NUMBER(38,0),
MENU_ITEM_NAME VARCHAR(16777216),
ITEM_CATEGORY VARCHAR(16777216),
ITEM_SUBCATEGORY VARCHAR(16777216),
COST_OF_GOODS_USD NUMBER(38,4),
SALE_PRICE_USD NUMBER(38,4),
MENU_ITEM_HEALTH_METRICS_OBJ VARIANT,
unique (MENU_ITEM_ID) rely,
primary key (MENU_ID) rely,
foreign key (MENU_TYPE_ID) references FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.MENU_TYPE(MENU_TYPE_ID) rely
);
-- create TRUCK HYBRID table which holds truck details
create or replace HYBRID TABLE FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.TRUCK (
TRUCK_ID NUMBER(38,0) NOT NULL,
MENU_TYPE_ID NUMBER(38,0),
PRIMARY_CITY VARCHAR(16777216),
REGION VARCHAR(16777216),
ISO_REGION VARCHAR(16777216),
COUNTRY VARCHAR(16777216),
ISO_COUNTRY_CODE VARCHAR(16777216),
FRANCHISE_FLAG NUMBER(38,0),
YEAR NUMBER(38,0),
MAKE VARCHAR(16777216),
MODEL VARCHAR(16777216),
EV_FLAG NUMBER(38,0),
FRANCHISE_ID NUMBER(38,0),
TRUCK_OPENING_DATE DATE,
primary key (TRUCK_ID) rely,
foreign key (MENU_TYPE_ID) references FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.MENU_TYPE(MENU_TYPE_ID) rely
);
-- create ORDER_HEADER HYBRID table which holds order information placed by customer
create or replace HYBRID TABLE FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.ORDER_HEADER (
ORDER_ID NUMBER(38,0) NOT NULL,
TRUCK_ID NUMBER(38,0),
CUSTOMER_ID NUMBER(38,0),
SHIFT NUMBER(38,0),
SHIFT_START_TIME TIME(9),
SHIFT_END_TIME TIME(9),
ORDER_CHANNEL VARCHAR(16777216),
ORDER_TS TIMESTAMP_NTZ(9),
SERVED_TS VARCHAR(16777216),
ORDER_CURRENCY VARCHAR(3),
ORDER_AMOUNT NUMBER(38,4),
ORDER_TAX_AMOUNT VARCHAR(16777216),
ORDER_DISCOUNT_AMOUNT VARCHAR(16777216),
ORDER_TOTAL NUMBER(38,4),
ORDER_STATUS VARCHAR(16777216) DEFAULT 'INQUEUE',
primary key (ORDER_ID) rely ,
foreign key (TRUCK_ID) references FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.TRUCK(TRUCK_ID) rely ,
foreign key (CUSTOMER_ID) references FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.CUSTOMER_LOYALTY(CUSTOMER_ID) rely ,
index IDX01_ORDER_TS(ORDER_TS),
index IDX02_ORDER_STATUS(ORDER_STATUS),
index IDX02_SHIFT(SHIFT)
);
-- create ORDER_DETAIL HYBRID table which holds order line item details
create or replace HYBRID TABLE FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.ORDER_DETAIL (
ORDER_DETAIL_ID NUMBER(38,0) NOT NULL,
ORDER_ID NUMBER(38,0),
MENU_ITEM_ID NUMBER(38,0),
DISCOUNT_ID VARCHAR(16777216),
LINE_NUMBER NUMBER(38,0),
QUANTITY NUMBER(5,0),
UNIT_PRICE NUMBER(38,4),
PRICE NUMBER(38,4),
ORDER_ITEM_DISCOUNT_AMOUNT VARCHAR(16777216),
primary key (ORDER_DETAIL_ID) rely ,
foreign key (ORDER_ID) references FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.ORDER_HEADER(ORDER_ID) rely ,
foreign key (MENU_ITEM_ID) references FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.MENU(MENU_ITEM_ID) rely
);
-- create our virtual warehouse
CREATE OR REPLACE WAREHOUSE tasty_unistore_app_wh AUTO_SUSPEND = 60;
-- use our TASTY_UNISTORE_APP_WH virtual warehouse so we can load our data
USE WAREHOUSE tasty_unistore_app_wh;
-- ingest from S3 into the MENU_TYPE HYBRID table
COPY INTO frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.menu_type
FROM @frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.s3load_unistore/raw_pos/menu/menu_type.csv.gz;
-- ingest from S3 into the MENU HYBRID table
COPY INTO frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.menu
FROM @frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.s3load_unistore/raw_pos/menu/menu.csv.gz;
-- ingest from S3 into the TRUCK HYBRID table
COPY INTO frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.truck
FROM @frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.s3load_unistore/raw_pos/truck/truck.csv.gz;
-- ingest from S3 into the CUSTOMER_LOYALTY HYBRID table
COPY INTO frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.customer_loyalty
FROM @frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.s3load_unistore/raw_customer/customer_loyalty/customer_loyalty_0_0_0.csv.gz;
-- ingest from S3 into the ORDER_HEADER HYBRID table
COPY INTO frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.order_header
FROM @frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.s3load_unistore/raw_pos/order_header/order_header_0_0_0.csv.gz;
-- ingest from S3 into the ORDER_DETAIL HYBRID table
COPY INTO frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.order_detail
FROM @frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.s3load_unistore/raw_pos/order_detail/order_detail.csv.gz;
-- view orders placed for a truck with truck id 81
SELECT *
FROM frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.order_header
WHERE truck_id = 81;
To ensure robust security measures, it is essential to establish a dedicated user account for the application, separate from your personal account. This new account will be utilized for querying Snowflake. Following best security practices, the account will employ key-pair authentication and be granted restricted access within the Snowflake environment.
Step 1: Generate Public and Private key for Authentication
Run the following commands to create a private and public key. These keys are necessary to authenticate the user with Snowflake.
$ cd ~/.ssh
$ openssl genrsa -out snowflake_app_key 4096
$ openssl rsa -in snowflake_app_key -pubout -out snowflake_app_key.pub
Step 2: Create the User and Role in Snowflake and Grant data access to this new Role
Execute the following SQL statements to create the user account and grant access to the data needed for the application.
-- use our securityadmin role
USE ROLE securityadmin;
-- create the tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo role
CREATE OR REPLACE ROLE tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo;
-- use our securityadmin role
USE ROLE accountadmin;
-- grant privileges to our tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo role
GRANT USAGE ON WAREHOUSE tasty_unistore_app_wh TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo;
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo;
GRANT UPDATE ON TABLE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore.raw.order_header TO ROLE tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo;
-- use our useradmin role
USE ROLE useradmin;
-- Open the ~/.ssh/snowflake_app_key.pub file from Step 1 and copy the contents starting just after the PUBLIC KEY header,
-- and stopping just before the PUBLIC KEY footer for INSERT_RSA_PUBLIC_KEY_HERE.It should be a single line string.
CREATE OR REPLACE USER data_app_unistore_demo
RSA_PUBLIC_KEY='<INSERT_RSA_PUBLIC_KEY_HERE>'
DEFAULT_ROLE=tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo
DEFAULT_WAREHOUSE=tasty_unistore_app_wh
MUST_CHANGE_PASSWORD=false;
-- use our securityadmin role
USE ROLE securityadmin;
GRANT ROLE tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo TO USER data_app_unistore_demo;
The application is structured around a 3-tier architecture, comprising a Persistence layer, Processing layer, and User Interface layer.
In the Persistence layer, Snowflake serves as the foundation, with an API developed to facilitate communication between the application and Snowflake. This communication is enabled through the Serverless Framework, Python, and Flask.
For the User Interface layer, React Native Framework is utilized, and the application is constructed using the Expo Framework.
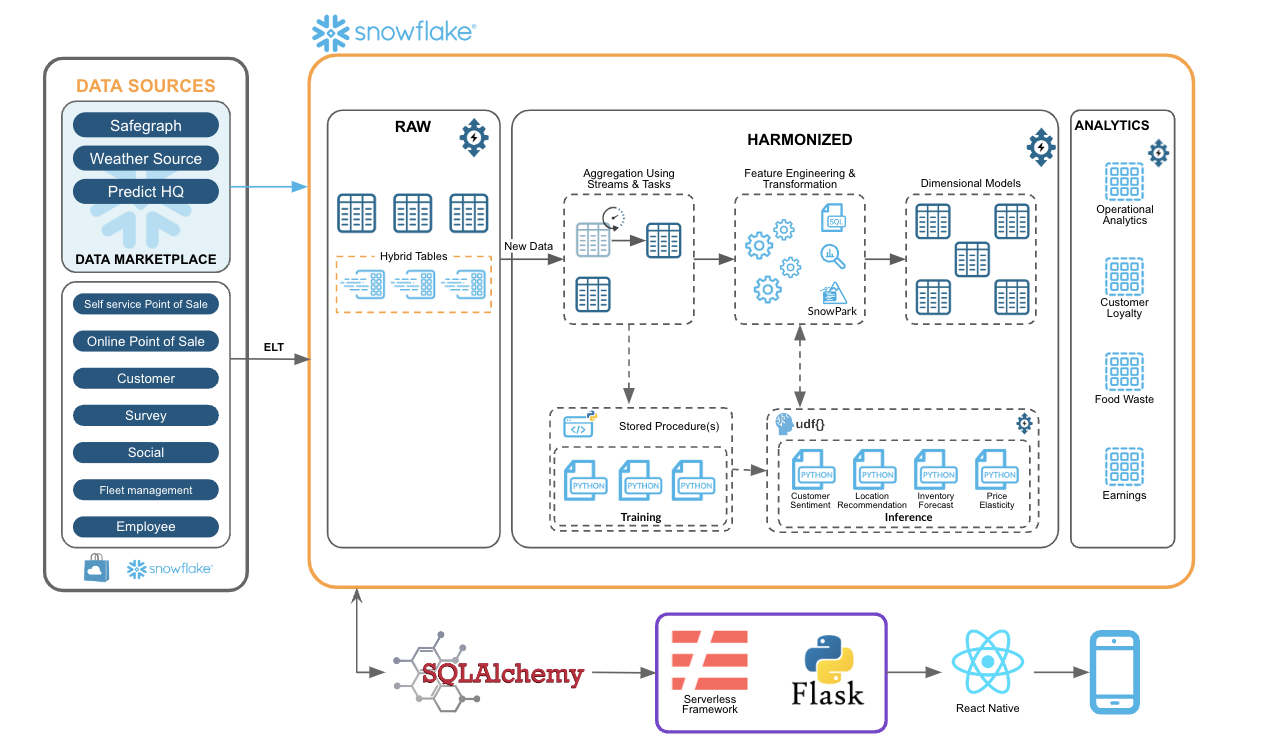
The application is versatile, capable of functioning as either a mobile or web application, compatible with iOS, Android, and Web platforms. Although designed for both, for demonstration purposes, it has been deployed as a Web Application.
To optimize the ordering process, our application relies on Snowflake's exclusive Unistore feature, leveraging hybrid tables at its core. These tables, seamlessly integrated into Snowflake's table types, are purpose-built for managing hybrid transactional and operational workloads, prioritizing minimal latency and enhanced throughput for small random point reads and writes.
Moreover, Hybrid Tables, currently accessible for public preview in select AWS regions, expedite rapid single-row operations, empowering teams to develop lightweight transactional use cases directly within Snowflake. This capability, combined with embedded indexes for swift data retrieval and enforced unique constraints for primary keys, significantly amplifies the efficiency of our application.
For Tasty Bytes food truck drivers, quick access to past and current orders, along with the ability to promptly update order statuses, is indispensable. Additionally, drivers require features such as viewing past earnings, sales comparisons, and monitoring food waste. The escalating success of these food trucks has driven up daily order volumes, thereby straining application performance and concurrent user support. Nevertheless, Unistore eliminates the need to duplicate or relocate data to handle transactional volume while providing analytical capabilities simultaneously. Furthermore, Snowflake's fully managed platform negates the necessity for managing infrastructure, query tuning, updates, or ensuring data continuity.
Step 1: Set up the Source Code
- Clone the repo using
git clone https://github.com/sf-gh-sjasti/TastyBytesReactNativeAppWithSnowflakeHybridTables.git reactNativeAppWithHybridTables - Navigate to the API folder to set up the backend Flask API,
cd reactNativeAppWithHybridTables/API - Run
npm installto install dependancies - Create a virtualenv to install python packages,
virtualenv venv --python=python3.8 - activate the virtualenv created,
source ./venv/bin/activate - Install the depenancies needed,
pip install -r requirements.txt - Update the private key in the
API/config.pyfile. ReplacePRIVATE_KEYwith the private key. Copy and paste the whole private key from~/.ssh/snowflake_app_keyincluding header(-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----) and footer(-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----). - Update
SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNTwith your Snowflake Account Locator. If you are located outside the us-west region, UpdateSNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNTasSNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT.CLOUD_REGION. You can get the Account Identifier from the Account URL. - Start the local serverless server,
node ./node_modules/serverless/bin/serverless wsgi serve - In a new Terminal Tab, Navigate to the UserInterface folder to set up the frontend React Native Application,
cd reactNativeAppWithHybridTables/UserInterface - Run
npm installto install dependancies - Run
npx expo start --clearand hitwkey to run the app in a web browser. If you are encountering "Error: error:0308010C:digital envelope routines::unsupported", Runexport NODE_OPTIONS=--openssl-legacy-provider - This launches the app in Web Browser
- Upon Launch, You can see the InQueue Orders Screen.
Step 2: Review the Source Code
We are using Key Pair Authentication to authenticate with Snowflake using SQL API. API/endpoints.py file has the API's we are using in the application. We are using SQLAlchemy to connect to the Snowflake. UserInterface/Orders.js has the source code to render Orders screen. OrderDetails.js has the source code to render Order Details Screen.
- Hybrid tables play a crucial role in the ordering process. Upon Launch of the application, You can see the InQueue Orders Screen. Now, let's delve into the development of this screen, starting with the Data Model. At the core of this Data Model are two primary tables. The first is the ORDER_HEADER table, which encompasses all orders placed by customers. Below, you'll find the definition of this table, outlining how it was created. Note that a primary key is mandatory for hybrid tables, and in this case, the ORDER_ID serves as the primary key.
create or replace HYBRID TABLE FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.ORDER_HEADER (
ORDER_ID NUMBER(38,0) NOT NULL,
TRUCK_ID NUMBER(38,0),
CUSTOMER_ID NUMBER(38,0),
SHIFT NUMBER(38,0),
SHIFT_START_TIME TIME(9),
SHIFT_END_TIME TIME(9),
ORDER_CHANNEL VARCHAR(16777216),
ORDER_TS TIMESTAMP_NTZ(9),
SERVED_TS VARCHAR(16777216),
ORDER_CURRENCY VARCHAR(3),
ORDER_AMOUNT NUMBER(38,4),
ORDER_TAX_AMOUNT VARCHAR(16777216),
ORDER_DISCOUNT_AMOUNT VARCHAR(16777216),
ORDER_TOTAL NUMBER(38,4),
ORDER_STATUS VARCHAR(16777216) DEFAULT 'INQUEUE',
primary key (ORDER_ID) rely ,
foreign key (TRUCK_ID) references FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.TRUCK(TRUCK_ID) rely ,
foreign key (CUSTOMER_ID) references FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.CUSTOMER_LOYALTY(CUSTOMER_ID) rely ,
index IDX01_ORDER_TS(ORDER_TS),
index IDX02_ORDER_STATUS(ORDER_STATUS),
index IDX02_SHIFT(SHIFT)
);
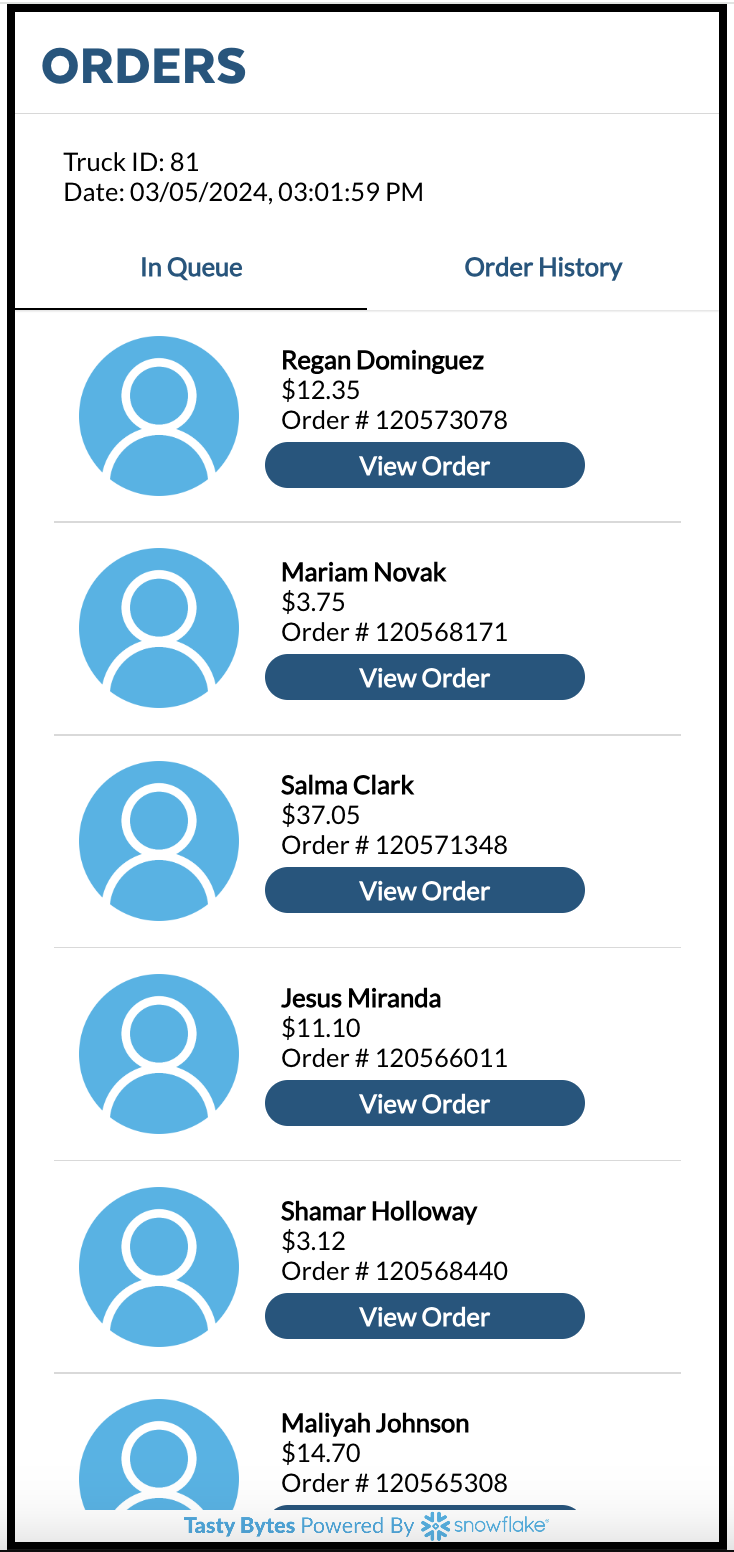
Hybrid tables also offer the capability to include secondary indexes. In our setup, we've indexed attributes such as TRUCK_ID, ORDER_TS, LOCATION_ID, and ORDER_STATUS. These indexes are instrumental in facilitating rapid lookups within the application, enhancing its responsiveness and user experience.
The second table in our setup is ORDER_DETAIL, which stores individual order line items within an order. It's common to have multiple order details associated with a single order header, especially when customers place multiple orders. The ORDER_DETAIL table includes ORDER_DETAIL_ID as its primary key and also features a foreign key, ORDER_ID, referencing the ORDER_HEADER table.
create or replace HYBRID TABLE FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.ORDER_DETAIL (
ORDER_DETAIL_ID NUMBER(38,0) NOT NULL,
ORDER_ID NUMBER(38,0),
MENU_ITEM_ID NUMBER(38,0),
DISCOUNT_ID VARCHAR(16777216),
LINE_NUMBER NUMBER(38,0),
QUANTITY NUMBER(5,0),
UNIT_PRICE NUMBER(38,4),
PRICE NUMBER(38,4),
ORDER_ITEM_DISCOUNT_AMOUNT VARCHAR(16777216),
primary key (ORDER_DETAIL_ID) rely ,
foreign key (ORDER_ID) references FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.ORDER_HEADER(ORDER_ID) rely ,
foreign key (MENU_ITEM_ID) references FROSTBYTE_TASTY_BYTES_APP_UNISTORE.RAW.MENU(MENU_ITEM_ID) rely
);
In our configuration, the hybrid table ensures referential integrity by enforcing constraints that validate the presence of a genuine order header record for each entry in the ORDER_DETAIL table. This mechanism guarantees that each order detail is associated with a valid and existing order header, maintaining data consistency and accuracy within the system.
You may also explore additional hybrid tables such as TRUCK, MENU, and CUSTOMER_LOYALTY.
- Click on the View Order button to access detailed order information. This action triggers a query on the hybrid table, employing point lookups to swiftly retrieve the specified order details.
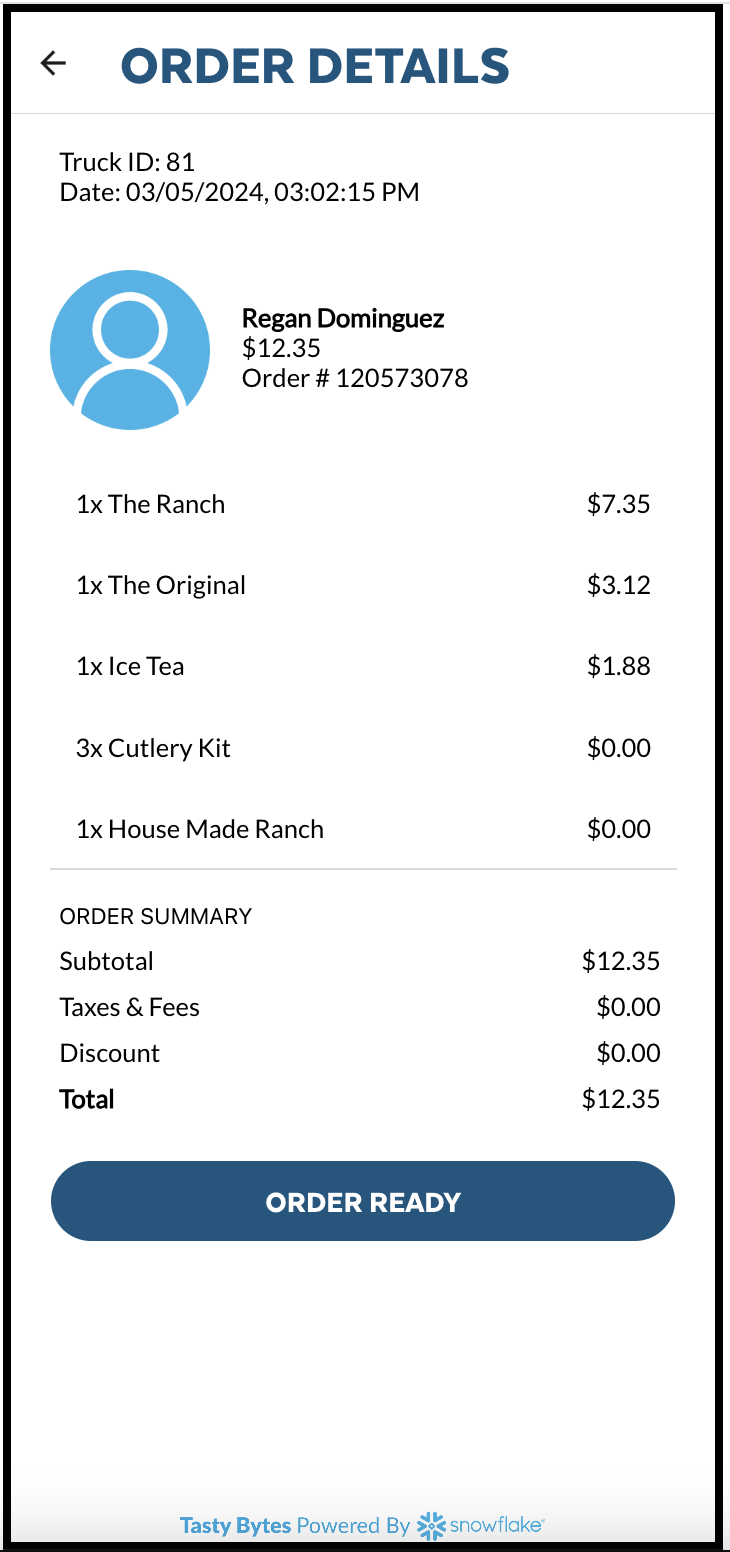
- Press the ORDER READY button to finalize the order. This initiates an update in the Hybrid Table, swiftly setting the Order Status value to Completed while utilizing rapid updates with row locking mechanisms. Afterward, you will be redirected back to the InQueue Orders Screen.
- Now, Click on Order History tab to see the completed orders.

Let's delve into an example illustrating how hybrid tables enforce Foreign Key Constraints and row locking.
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Step 1 -
Let's explore how Foreign Key enforcement operates in conjunction with hybrid tables.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
-- first set our role and warehouse context
USE ROLE accountadmin;
USE WAREHOUSE tasty_unistore_app_wh;
USE DATABASE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore;
/*
Let's take a look at tables, order_header and order_detail, where order_detail has a foreign key
order_id referencing the order_id column in the order_header table. Let's observe how a hybrid table
restricts the insertion of an order_detail record with an order_id that does not exist in the
order_header table. This will demonstrate how hybrid tables enforce foreign key constraints.
*/
-- let's review the definition of the order_header table
SELECT get_ddl('table', 'raw.order_header');
-- let's now examine the definition of the order_detail table
SELECT get_ddl('table', 'raw.order_detail');
-- insert a record into the order_header table.
INSERT INTO raw.order_header
(
ORDER_ID, TRUCK_ID, CUSTOMER_ID, SHIFT,
ORDER_TS, SERVED_TS, ORDER_CURRENCY, ORDER_AMOUNT, ORDER_TAX_AMOUNT,
ORDER_DISCOUNT_AMOUNT, ORDER_TOTAL, ORDER_STATUS
)
VALUES
(
23764646, 81, 129999, 0,
'2024-02-20 12:25:51.360', NULL, 'USD', 15.4700, NULL,
NULL, 15.4700, 'INQUEUE'
);
-- insert a record into the order detail table with an order ID that does not exist in the ORDER_HEADER table.
-- upon attempting this insertion, you will encounter a violation indicating that the
-- foreign key constraint "SYS_INDEX_ORDER_DETAIL_FOREIGN_KEY_ORDER_ID_ORDER_HEADER_ORDER_ID" has been violated.
INSERT INTO raw.order_detail
(
ORDER_DETAIL_ID, ORDER_ID, MENU_ITEM_ID, LINE_NUMBER,
QUANTITY, UNIT_PRICE, PRICE, ORDER_ITEM_DISCOUNT_AMOUNT
)
VALUES
(
558148642, 23764647, 61, 5,
2, 17.21, 34.42, null
);
-- insert a record into the order_detail table using the order ID from the previously created order.
-- after executing this insertion, you should observe that the record is successfully inserted.
INSERT INTO raw.order_detail
(
ORDER_DETAIL_ID, ORDER_ID, MENU_ITEM_ID, LINE_NUMBER,
QUANTITY, UNIT_PRICE, PRICE, ORDER_ITEM_DISCOUNT_AMOUNT
)
VALUES
(
558148642, 23764646, 61, 5,
2, 17.21, 34.42, null
);
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You've seen how Hybrid Tables have been utilized in a lightweight transactional application
to enforce referential integrity through foreign key constraints. These constraints ensure
that relationships between tables remain consistent, particularly between related tables
such as the order header and order detail tables. By defining foreign key constraints, the database
ensures that every order detail record references a valid order ID from the order header table.
This not only maintains data integrity but also provides a reliable framework for querying and
analyzing related data. Overall, the integration of foreign key constraints with hybrid tables
enhances the application's data consistency and reliability, laying a solid foundation for
robust transactional processing.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Step 2 -
Now, let's delve into how row locking operates by initiating a lock on a specific row,
subsequently updating that locked row, and then proceeding to update a different row.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
-- lock the order created earlier while performing an update, but refrain from executing the commit operation yet.
-- pick an Order id from the Orders Tab in the frontend Driver Application.
BEGIN;
UPDATE raw.order_header
SET order_status = 'COMPLETED'
WHERE order_id = '<Order Id from the App>';
-- Navigate to the frontend application.
-- Choose any order other than the one you picked Earlier to Update and click on the "View Order" button corresponding to the order.
-- Click on the "Order Ready" button to update the order.
-- This will Complete the order successfully.
-- Next, click on the "View Order" button for the previously locked order from above.
-- Attempt to update the order by clicking on the "Order Ready" button.
-- You will observe that the API call times out after waiting for the specified 180-second timeout period.
-- Now, commit the transaction, and you will notice the order being successfully updated.
COMMIT;
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In summary, our actions have illustrated the row locking capability of hybrid tables
within a transactional context. We've witnessed the locking of a specific order during
an update operation, ensuring data integrity and preventing concurrent modifications
until the transaction is committed.
Furthermore, our scenario also hints at the ability to update other rows concurrently,
showcasing the flexibility and efficiency of hybrid tables in handling concurrent transactions
while maintaining data consistency.
Overall, this demonstrates the robustness and reliability of hybrid tables in
supporting transactional applications.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
Navigate to Snowsight Worksheets, click "+" in the top-right corner to create a new Worksheet, and choose "SQL Worksheet". Paste and run the following SQL in the worksheet to drop Snowflake objects created in the Quickstart.
USE ROLE accountadmin;
DROP DATABASE frostbyte_tasty_bytes_app_unistore;
DROP WAREHOUSE tasty_unistore_app_wh;
DROP USER data_app_unistore_demo;
DROP ROLE tasty_bytes_data_app_unistore_demo;
Conclusion
You did it! You have successfully completed the Tasty Bytes - Developing React Native Application using Snowflake Hybrid Tables Quickstart.
By doing so you have learned:
- Developing Data Applications leveraging Snowflake Hybrid Tables
- Authenticating with Snowflake using Key Pair Authentication
- Leveraging SQLAlchemy to connect to Snowflake from the Application
- Developing Flask API's
- Developing React Native Application
Next Steps
To continue your journey in the Snowflake Data Cloud, please visit the link below to see more Tasty Bytes - Quickstarts available to you.